Safer and more long-term effective iNSC DAP Parkinson's cell therapy
Parkinson's disease (PD) is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases. Epidemiology shows that the prevalence rate is 15-328/100000 people, the average age of onset is 60 years old, and the incidence rate of people over 65 years old is 1.7%. The average life expectancy of PD patients after diagnosis is 7-14 years. In 2005, there were approximately 2 million PD patients in China, and it is expected that by 2030, the number of PD patients in China will approach 5 million, while the global number of PD patients will exceed 8.7 million. The etiology and pathogenesis of PD are not yet clear, and may be related to genetic, environmental, and social factors.
The main pathological changes of PD are degenerative changes and loss of dopamine (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain, loss of pigmentation in locus coeruleus neurons, fading of melanin and appearance of Lewy bodies. The neurobiochemical changes of PD are the loss of DA neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain, leading to a significant decrease in DA content in the striatum, while acetylcholine, which antagonizes DA function, is relatively overactive in the nigrostriatal system. The balance between DA and acetylcholine is disrupted, resulting in motor dysfunction.
The main clinical manifestations include motor symptoms and non motor symptoms. Motor symptoms mainly include static tremors, muscle rigidity or increased muscle tone, bradykinesia, and abnormal posture and gait. Non motor symptoms mainly include cognitive/psychiatric disorders (such as depression or anxiety), sleep disorders, autonomic dysfunction, and sensory disorders. PD brings great pain to patients themselves and imposes a heavy burden on families and society.
However, there is currently no effective treatment plan for PD in clinical practice. The main treatment method is symptomatic treatment, starting from reducing pain, delaying disease development, and improving patients' quality of life. Stem cell therapy is expected to become an effective way to treat Parkinson's disease due to its ability to supplement and replace missing dopaminergic neurons, restore neuronal signal transduction.

Neural stem cells are a type of stem cell derived from the nervous system, with self-renewal ability. It can generate offspring and differentiate into neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and other nerve cells through asymmetric cell proliferation and differentiation.
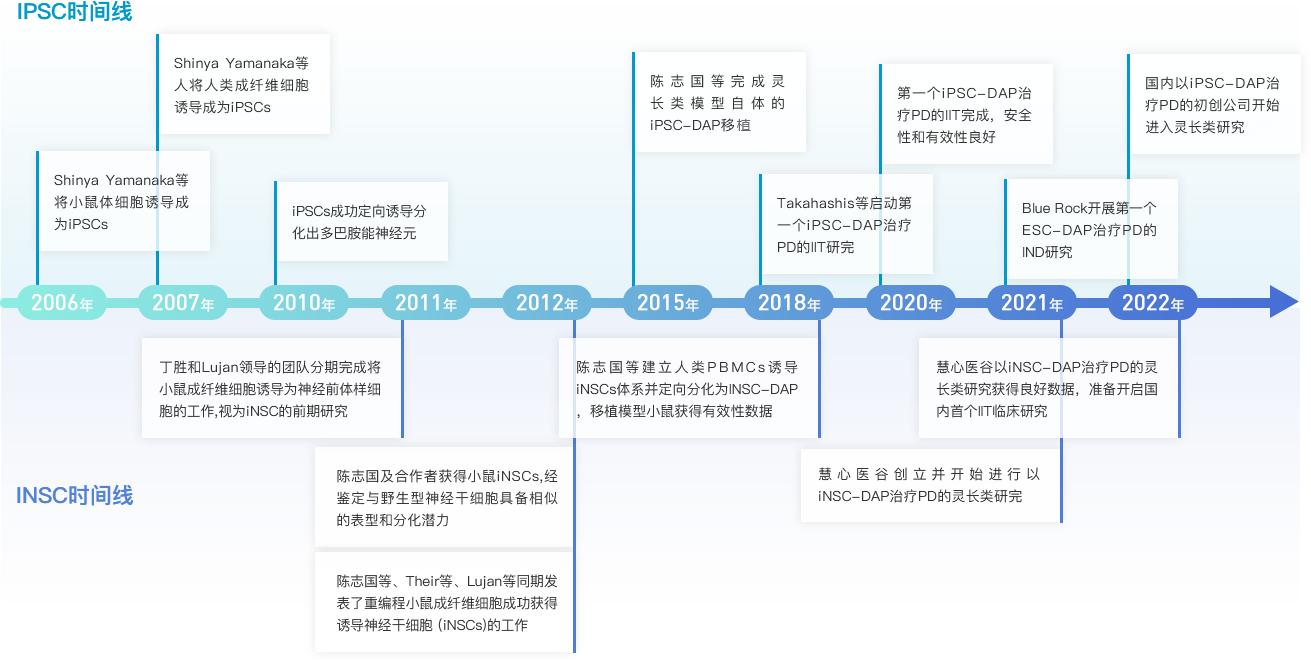
Using cell reprogramming technology platform and neural cell differentiation platform, neural stem cells (iNSCs) were obtained from adult blood cells as seed cells for autologous transplantation, which can be used for targeted treatment of various neurological diseases and injuries such as Parkinson's. In this way, we can also address the issue of insufficient sources of neural stem cells and ethical concerns.
INSCs technology has complete independent intellectual property rights and holds multiple invention patents in China and the United States. The discovery of neural stem cells and their isolation and transplantation for disease treatment have brought new hope for the treatment of various neurological diseases, especially neurodegenerative diseases.
Copyright © Beijing Huixin Wiseheart Medval Biotechnology Co., Ltd